Global drylands and soil resource poverty
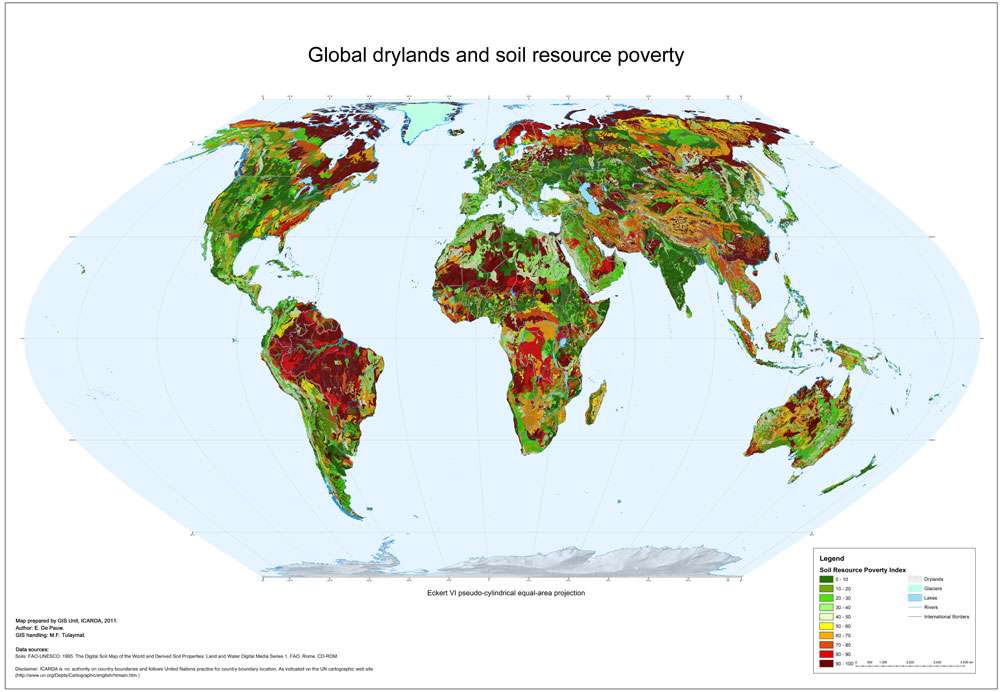
The Soil Resource Poverty Index is the percentage of each grid cell occupied by problem soils. Problem soils include the following categories: saline soils, soils with high sodium content, shallow soils, sandy soils, soils with very poor profile development, soils with severe soil structural and/or textural limitations, soils with severe acidity, infertility or Al-toxicity problems, wetland soils, acid sulphate soils.
Author:
E. De Pauw
Institute:
ICARDA GIS unit
Decription:
The Soil Resource Poverty Index is the percentage of each grid cell occupied by problem soils. Problem soils include the following categories: saline soils, soils with high sodium content, shallow soils, sandy soils, soils with very poor profile development, soils with severe soil structural and/or textural limitations, soils with severe acidity, infertility or Al-toxicity problems, wetland soils, acid sulphate soils.
In the classification of the FAO Soil Map of the World this translates as:
Group 1: Saline soils
All Solonchaks and salt flats
Soil units: Z, Zg, Zt, Zm, Zo, SALT
Group 2: Soils with high sodium content
All Solonetz+ SolodicPlanosols
Soil Units:S, Sg, Sm, So, Ws
Group 3: Shallow soils
All Lithosols, Rendzinas, Rankers and rock outcrops
Soil units: I, E, U, ROCK
Group 4: Sandy soils
Dunes and shifting sands, sandy soils in arid environments, highly leached sandy soils in more humid environments
Soil units: DS, Qa, [Ql, Qf, Qc if aridity index <.2]
Group 5: Soils with very poor profile development
Regosols
Soil units: R, Rx, Rc, Rd, Re
Group 6: Soils with severe soil structural and/or textural limitations
Planosols
Soil units: W, Wm, Wh, Wd, We
Group 7: Soils with severe acidity, infertility or Al-toxicity problems
All Ferralsols and Acrisols, except ‘humic’ subgroups; all Podzols and Podzoluvisols
Soil units: F, Fp, Fa, Fr, Fx, Fo, A, Ap, Ag,Af, P, Pp, Pg, Ph, Pf, Pl, Po, D, Dg, Dd, De
Group 8: Wetland soils
Histosols, some Gleysols
Soil units: O, Ox, Od, Oe, Gx, Gp
Group 9: Acid sulphate soils
Soil unit: Jt
Under the decision rules for defining the SRPI, soils that have specific management needs but are productive under appropriate management are not considered problem soils. Examples of soils with special management needs are Vertisols (which require relatively low-cost practices promoting good drainage), acid soils (which require adapted fertilization), erosion-prone soils (which require soil conservation measures) or stony soils (which require stone clearance, as is already standard practice in many parts of the region).
Source Data:
FAO-UNESCO. 1995. The Digital Soil Map of the World and Derived Soil Properties. Land and Water Digital Media Series 1. FAO, Rome. CD-ROM.


